On the Formal Analysis of Geometrical Optics in HOL
Geometrical optics, in which light is characterized as rays, provides an efficient
and scalable formalism for the modeling and analysis of optical and laser systems.
The main applications of geometrical optics are in stability analysis of optical
resonators, laser mode locking and micro opto-electro-mechanical systems.
Traditionally, the analysis of such applications has been carried out by informal
techniques like paper-and-pencil proof methods, simulation and computer algebra systems.
These traditional techniques cannot provide accurate results and thus cannot be
recommended for safety-critical applications, such as corneal surgery, process
industry and inertial confinement fusion. On the other hand, higher-order logic
theorem proving does not exhibit the above limitations, thus we propose a higher-order
logic formalization of geometrical optics. Our formalization is mainly based on theories
of multivariate analysis in the HOL Light theorem prover. In order to demonstrate the practical
effectiveness of our formalization, we present the modeling and stability analysis of
some optical resonators in HOL Light.
HOL Light Script
- utilities.ml (This file contains some useful tactics which are used in our formalization)
- geometrical_optics.ml (This file contains the formalization of underlying theory of geometrical optics)
- component_library.ml (This file contains the formalization of frequently used optical components)
- resonator.ml (This file contains the formalization of optical resonators and their stability)
Core Formalization
Applications
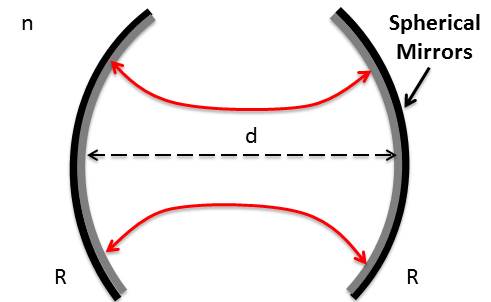
1. Fabry Perot Resonator with Spherical Mirrors